Introduction
EV Charging Infrastructure USA 2025 is gaining momentum across the United States, with millions of drivers transitioning from gasoline-powered vehicles to eco-friendly electric alternatives. However, the success of EV adoption is not just about advanced car technology; it depends heavily on a robust and accessible EV charging infrastructure.
The USA is investing billions of dollars to expand its charging network, aiming to support President Biden’s target of having 500,000 public charging stations by 2030. As of 2025, the country has already made remarkable progress, but challenges remain in terms of coverage, charging speed, and affordability.
This article provides a complete analysis of the EV charging infrastructure in the USA, covering its current status, growth projections, key players, government initiatives, cost factors, and the future roadmap.
Why EV Charging Infrastructure Matters in the USA
The transition to EVs is not possible without a reliable and widespread charging network. Unlike gas stations, which are available almost everywhere, EV charging stations are still unevenly distributed.
Key Reasons Why EV Charging Infrastructure is Critical:
-
Range Confidence: Drivers need assurance they won’t run out of power.
-
Adoption Boost: A larger charging network encourages more EV purchases.
-
Sustainability: EV adoption reduces carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Economic Growth: Expanding infrastructure creates jobs and attracts investments.
Current Status of EV Charging Infrastructure in the USA (2025)
As of early 2025, the USA has seen exponential growth in EV charging stations.
Table 1: Current EV Charging Network in the USA (2025 Estimates)
| Type of Charger | Number of Stations | Typical Charging Time | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (120V) | ~30,000+ | 8–20 hours | Home charging |
| Level 2 (240V) | ~90,000+ | 4–8 hours | Public/workplace |
| DC Fast Charging (480V) | ~28,000+ | 30–60 minutes | Highway travel |
Source: U.S. Department of Energy, EV Charging Infrastructure Reports 2025
This network is expected to expand further as government and private companies ramp up investments.
Types of EV Charging Stations in the USA
To understand the infrastructure better, let’s break down the three main types of EV chargers available:
1. Level 1 Charging
-
Uses a standard household outlet (120V).
-
Very slow – up to 5 miles of range per hour.
-
Best for overnight home charging.
2. Level 2 Charging
-
Requires a 240V outlet.
-
Provides 15–30 miles of range per hour.
-
Commonly found at homes, workplaces, and public stations.
3. DC Fast Charging (DCFC)
-
Provides rapid charging with 100+ miles of range in 30 minutes.
-
Ideal for highways, long trips, and commercial fleets.
-
More expensive to install but critical for nationwide adoption.
Government Support and Policies
The U.S. government is playing a pivotal role in expanding EV charging infrastructure.
Key Initiatives:
-
National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program
-
$5 billion allocated to build a national charging network.
-
Focused on major highways and rural access.
-
-
Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (2021)
-
Includes funding for 500,000 public chargers by 2030.
-
-
Tax Credits & Incentives
-
Businesses and individuals installing EV chargers can claim tax benefits.
-
-
State-Level Programs
-
States like California, New York, and Texas lead in charging infrastructure investments.
-
Key Players in the U.S. EV Charging Market
Several companies are competing and collaborating to build a seamless charging experience for EV owners.
Table 2: Major EV Charging Companies in the USA
| Company | Charging Network Size | Specialty | Notable Partnerships |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Supercharger | ~25,000+ | Fast charging, Tesla exclusive (some opened to others) | Partnerships with Ford, GM |
| Electrify America | ~4,000+ stations | High-speed charging | Backed by Volkswagen |
| ChargePoint | ~30,000+ ports | Workplace & public | Works with fleets and businesses |
| EVgo | ~3,000+ fast chargers | Renewable-powered stations | GM partnership |
| Blink Charging | ~8,000+ stations | Level 2 and fast charging | Nationwide coverage |
These networks ensure drivers have multiple charging options across states.
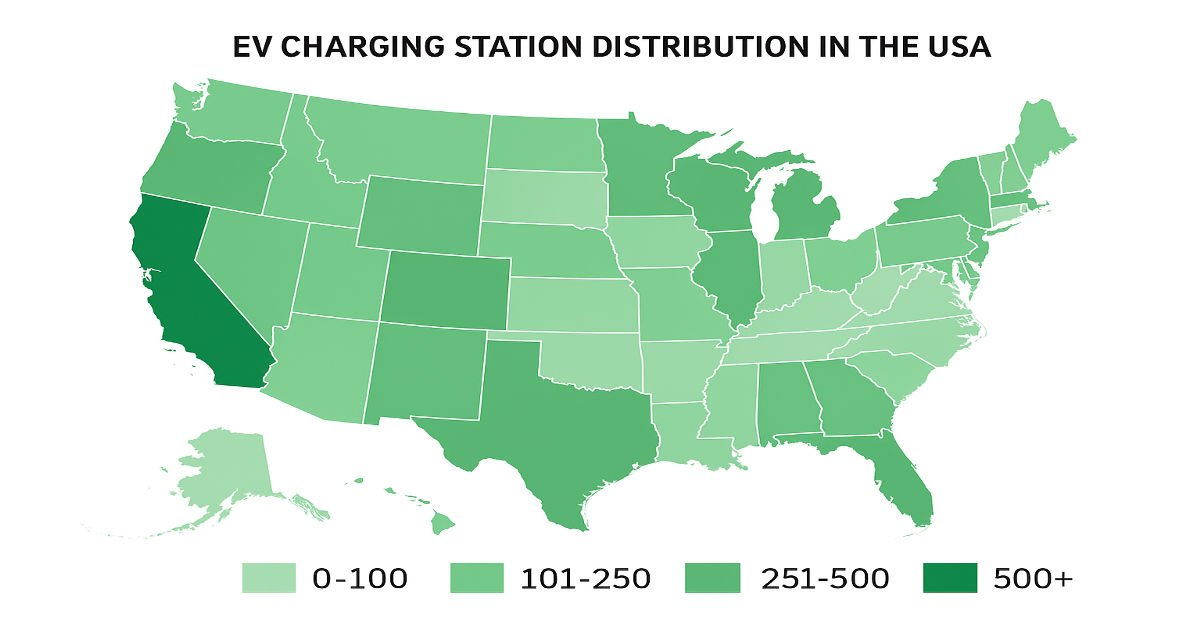
Regional Distribution of EV Charging Stations
EV infrastructure is not evenly spread across the country.
-
California: Leading state with over 40,000+ charging ports.
-
New York & Texas: Expanding rapidly due to government funding.
-
Rural Areas: Still face infrastructure gaps, limiting adoption.
Cost of EV Charging in the USA
The cost of charging an EV varies depending on location, charging speed, and electricity rates.
Table 3: Average EV Charging Costs in the USA (2025)
| Charging Type | Average Cost per kWh | Cost for Full Charge (60 kWh Battery) |
|---|---|---|
| Home Charging (Level 2) | $0.13 | $7.80 |
| Public Level 2 | $0.20 – $0.25 | $12 – $15 |
| DC Fast Charging | $0.30 – $0.50 | $18 – $30 |
⚡ Note: Some charging networks also charge per-minute fees instead of per kWh.
Challenges Facing EV Charging Infrastructure
Despite growth, the U.S. faces significant challenges:
-
Unequal Distribution – Urban areas are well covered, rural areas lag.
-
High Installation Costs – DC fast chargers can cost $40,000 – $100,000 per unit.
-
Grid Capacity Issues – Widespread EV adoption requires grid upgrades.
-
Interoperability – Not all chargers support all EV models.
-
Charging Speed – While improving, charging still takes longer than refueling with gas.
The Future of EV Charging Infrastructure in the USA
Looking ahead, the U.S. is expected to see massive growth in EV charging networks.
Predictions for 2030:
-
500,000+ public charging stations nationwide.
-
Faster charging speeds with 350kW+ ultra-fast chargers.
-
Wireless charging at select locations.
-
Smart charging grids that balance electricity demand.
-
EV-to-grid (V2G) technology allowing cars to supply energy back.
Consumer Tips: How to Find EV Charging Stations
Drivers can use apps and networks to locate charging points easily.
Popular EV Charging Apps in the USA:
-
PlugShare
-
ChargePoint
-
EVgo
-
Electrify America
-
Google Maps (integrated EV charging locator)
Environmental Impact of EV Charging
-
EVs powered by renewable energy reduce emissions significantly.
-
The shift to solar, wind, and hydro-powered stations enhances sustainability.
-
Some networks (like EVgo) already operate on 100% renewable energy.
Conclusion
EV Charging Infrastructure USA 2025 is undergoing a rapid transformation. With strong government support, private investment, and technological innovation, the future looks promising.
However, challenges like grid upgrades, rural coverage, and cost reduction must be addressed to ensure seamless adoption.
By 2030, the USA aims to build one of the world’s largest EV charging networks, supporting millions of electric vehicles and driving the nation toward a cleaner, sustainable transportation future.